Theme: An insight into the Recent Research and cutting-edge Technologies in Lasers, Optics and Photonics
Laser Optics 2022
Welcome to the European Congress on Laser, Optics and Photonics (Hybrid Conference) and also join the conference using online platforms during November 24-25, 2022 as a Webinar. LASER OPTICS 2022 is being organized with the association of Research Journal of Optics and Photonics where all the conference abstracts will be published.
Research Journal of Optics and Photonics is a multidisciplinary journal that combines physical sciences with material sciences, engineering and technology. The journal encourages the latest developments and innovations for publication on the open access platform as research articles, reviews, case studies, commentaries, short communication and the letters to the editor.
The theme of the conference highlights “An insight into the Recent Research and cutting-edge Technologies in Lasers, Optics and Photonics”. Scientific Tracks designed for this conference will enable the attendees and participants to learn extremes.
Importance & Scope:
Lasers, Optics, and Photonics have not only aided in the advancement of several sectors of science and technology, but have also made significant contributions to the betterment of human life quality. All of this is possible because to many discoveries and inventions that have led to the creation of various applications. The main goal of the Laser Optics conference is to allow participants to network, communicate, and exchange new ideas in the domains of lasers, optics, and photonics.
Why to attend Laser Optics 2022?
Laser Optics 2022 provides a platform for globalizing research by facilitating dialogue between companies and academic institutions, as well as information transmission from research to industry. Laser Optics 2022 intends to disseminate knowledge and new ideas among experts, industrialists, and students working in the fields of lasers, optics, and photonics by allowing them to share their research experiences and participate in interactive discussions and special sessions.
Target Audience:
- Eminent Scientists/Research Professors in the field of lasers, Optics & photonics
- Junior/Senior research fellows in Lasers, Optics & photonics, Students
- Directors of Photonics companies
- Photonics Engineers
- Members of different Lasers, Optics and Photonics associations
Track 01 : Laser System
A laser is a device that uses energy to transmit light at specified wavelengths and amplifies that light by generating a very narrow beam of radiation. Light is an electromagnetic wave, as we all know. Each wave has its own brightness and colour, and polarisation shivers at a specific place. "Light enhancement by fortified emissions of radiation" is what laser stands for. When electrons in molecules in glassware, jewels, or gases retain vitality from an electrical current or another laser, they get "stimulated" and form a laser. The energized electrons exchange from a lower-energy circle to a higher-energy circle around the atom’s core. White light encases all colors within the range, but indeed a coloured light, such as a ruddy Driven contains a frequented interim of ruddy wavelengths. Laser is called continuous-wave.
Types of lasers:
Track 02 : Optics and Lasers in Medicine
Optical fibre medical equipment may have optical fibre bundles. Endoscope is an optical fibre equipment that is used to see the inner workings of the human body. The endoscope allows surgeons to view into the body without having to perform surgery.
The use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as PDT, is known as laser medicine. After light activation, photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a two-stage treatment that combines light energy with a medication (photosensitizer) to kill malignant and precancerous cells. Initial laser beam tests revealed that a precisely focused beam from a carbon dioxide gas laser could effortlessly and skillfully cut through human flesh. As a result, the beam is the ideal equipment for performing difficult surgeries as a backup to the traditional blade. Lasers were thought to be most effective in working on portions of the body that are easy to reach, such as the ears, skin, lips, eyes, and nose.
• Photodynamic therapy with lasers
• Photorejuvenation with lasers
Track 03 : Optoelectronics
The quantum mechanical effects of light on electronic materials, semiconductors, and in the presence of electric fields are the basis of optoelectronics. Electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical transducers are optoelectronic devices. It is in the sphere of technology that light is linked to power. Optoelectronics is a rapidly expanding technology sector in which electronic devices are used to source, detect, control, and mechanise light. Electronic devices for emitting, modulating, transmitting, and sensing light are included in this discipline of electronics.
Optoelectronics Technologies:
Track 04 : Optical communications and networking
Optical telecommunication is another name for optical communication. Light communication is used to send information over a long distance. Optical networking systems, which include optical fibre, optical amplifiers, lasers, switches, routers, and other related technologies, are critical in modern communications. Telecom businesses employ optical fibre to transmit telephone signals, internet connectivity, and cable TV signals. It's also employed in medical, defence, government, industrial, and commercial settings. Tunable filters, termination devices, optical amplifiers, transceivers, and add-drop multiplexers are among the optical components that are becoming increasingly dependable and affordable. To address the electrical blockage at network edges, optical technologies are gradually being included into access networks and metropolitan area networks. Single mode, multimode, and polymeric optical fibre are the three most common types of fibre optic cable utilised here.
Track 05 : Advancements in Photonics
Photonics and Optics is the current science of photon generation, detection, and exploitation via emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, detection/sensing, and behaviour, as well as light qualities. A prospective application of photonics that is currently being investigated instead of electronics. Converting electrons to photons has a number of advantages, the most important of which is speed. The usage of photonics, which has been shown to be more energy-efficient than conventional technologies, is the next step in the increasing speed of technology. It includes laser manufacturing, biological and chemical sensing, medical diagnostics and therapy, display technologies, and optical computing, among other science and technology applications.
Track 06 : Nano Photonics and Bio Photonics
Nanophotonics is the study of light's effects on the nanoscale scale and how light interacts with matter at that scale. Optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology all fall under the umbrella of Nano Photonics. Surface plasmon polaritons can transport and focus light via dielectric structures such as nano antennas or metallic components. Photonic crystal devices, such as dielectric nanophotonic structures and electronics, enabling wavelength-scale light manipulation.
Bio Photonics is the study and application of optical techniques, primarily for imaging. The study of biological molecules, cells, and tissues is referred to as biology. It is a multidisciplinary field that studies the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with biological materials in living creatures, such as tissues, cells, subcellular structures, and chemicals. Bio photonics is a technique that uses a beam of light, such as a laser or an LED, to allow surgeons to view how cells and tissues work. For diagnosis, treatment, and surgery, this light approach provides a sample of damaged and healthy tissue.
Track 07 : Quantum Science and Technology
Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics concerned with the behaviour of matter and light at the atomic and subatomic levels. Quantum technology is a branch of science that employs quantum physics, as well as quantum entanglement and quantum superposition. It is based on the ability to manipulate individual quantum systems in order to exploit occurrences. By manipulating, producing, and calculating single photons as well as quantum systems that emit photons, quantum photonics aims to uncover the essential properties of quantum mechanisms and contribute to the development of future photonic quantum technologies. It can work by manipulating matter at extremely small sizes, and it is reliant on and supported by breakthroughs in nanotechnology.
- Quantum computing
- Quantum sensors
- Quantum cryptography
- Quantum simulation
- Quantum metrology
- Quantum imaging
Track 08 : Technologies in Lasers, Optics and Photonics
Optical technology refers to everything that has to do with light or vision, whether it's visible light or infrared light that serves a purpose. Mouse, for instance, is an optical device that makes use of optical technology. Laser and photonics technology is a highly technical degree that focuses on teaching students how to use electronic, fibre optic, photonic, and laser principles in real-world situations. Optical disc drives, laser printers, barcode scanners, DNA sequencing devices, fiber-optic, laser surgery and skin treatments, cutting and welding materials, military, and measuring range and speed are all examples of laser applications.
- LiDAR
- Optical Tweezers
- Laser Scalpel
- Laser Cutters
- Laser Welding
- Fiber Optics
- Optical Storage
- 3D Scanners
- Ultra-Fast Photography
Track 09 : Applications and Trends in Optics and Photonics
- Chemical synthesis, medical diagnostics, on-chip data communication, sensors, laser defence, and fusion energy are just a few of the latest uses of photonics.
- Optical instrumentation
- Optical fabrication
- Optics in astronomy and astrophysics
- Integrated photonics
- Diffractive optics
- Computational optical sensing and imaging
- Optical imaging
- Applied optics
Track 10 : Fiber Laser Technology
A fibre laser is a laser with an optical fibre doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium, and holmium as the enthusiastic pickup medium. Fiber lasers are unique from other laser types for the most part. A fibre laser is a type of laser in which the pillar and the laser depression are combined into a single framework inside an optical fibre, with the pillar created within the fibre.
Track 11 : Optical physics
Optical physics is the nature study of the fundamental assets of light and its interaction with matter. This contains typical optical phenomena such as reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. It includes the study of sight. It varies from general optics, optical engineering and among them there are optical physics, applied optics, and optical engineering. The uses of applied optics and the devices of optical engineering are necessary for basic research in optical physics, and that research takes to the development of new devices and applications.
The study of the creation of electromagnetic radiation, its properties, and its interaction with matter, particularly its manipulation and control, is referred to as optical physics. However, there is no clear separation between optical physics, applied optics, and optical engineering, because optical engineering devices and applied optics applications are required for basic optical physics research, which leads to the development of novel devices and applications. Light creation and detection, linear and nonlinear optical processes, and spectroscopy are all part of this subject. Optical science has been changed by lasers and laser spectroscopy. Quantum optics and coherence, as well as femtosecond optics, are hot topics in optical physics. The nonlinear response of single atoms to strong, ultra-short electromagnetic fields, the atom-cavity interaction at high fields, and quantum features of the electromagnetic field are all supported in optical physics.
Track 12 : Optical Fiber
A flexible, see-through fibre made of silica glass or plastic with a diameter slightly larger than that of a human hair is known as an optical fibre. The wave guide is comprised of translucent dielectrics and is used for optical communication. Optical fibres are widely employed in fiber-optic communications and are primarily utilised to transfer light between the two ends of the fibre.
Types of Fiber optics:
- On the basis of the Number of Modes
- Single-mode fiber
- Multi-mode fiber
- On the basis of Refractive Index
- Step-index optical fiber
- Graded index optical fiber
Track 13 : Surface Enchanced Spectroscopy
SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy) is a surface-sensitive technique for enhancing raman scattering by molecules absorbed on rough metal surfaces or nanostructures such plasmonic magnetic silica nanotubes. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering is another name for it. SERS substrates can identify proteins in physiological fluids since they are utilised to detect the presence of low abundance bio molecules. SERS has been used to detect urea and blood plasma label-free in human serum, and it could be the next step in cancer detection and screening. SERS is a technique for determining molecular system structural information. It's used in a variety of fields, including ultrasensitive chemical sensing and environmental studies.
Track 14 : Bio and Medical Optics
Biomedical optics is a branch of optics that focuses on the use of light in biological research and medicine, as well as the creation of the optical tools required to do so. Optics, lasers, and information technology have recently made biomedical imaging faster and less expensive, as well as reducing the need for surgery. The study of how light is directed into biological tissues is known as biomedical. Laser and optics biomedical technologies include biological research, medical diagnostics, and therapeutic applications.
- Biosensors
- Nonlinear Optical Microscopes
- Image Restoration
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Super-Resolution of Retinal Images
- Novel Sources for Multiphoton Microscopy
- Optical Coherence Tomorgraphy and Microscopy
- Fluorescence Imaging of Gene Expression
Track 15 : Optical Engineering
Optical Engineering is a branch of science and engineering that studies the physical phenomena and technologies involved in the generation, transmission, manipulation, detection, and use of light. Optical engineers utilise optics to solve problems, develop, and create products that employ light to conduct meaningful work. They build and run optical equipment such as lenses, microscopes, telescopes, lasers, detectors, fibre optic communication systems, and optical disc systems that use the properties of light and are based on physics and chemistry (Example: CD, DVD).Optical Engineering metrology use optical technologies to detect micro vibrations using devices such as the laser speckle interferometer or mass characteristics with refraction instruments. Nano-Measuring and Nan-Positioning equipment were developed by Optical Engineers.
Track 16 : Nano and Micro Optics
The subject of nano-optics benefits from the convergence of advances in fundamental physics, particularly quantum optics, classical and micro-optics, and enhanced fabrication technologies. In contrast to mainstream nanotechnology, the prefix "nano" for optics does not always imply the use of nanometer-scale structures, where smaller is always better; the designation is frequently used for optical systems with sizes shorter wavelength, and thus is sometimes referred to as subwavelength optics. We'll look at micro- and nano-optical concepts with size scales ranging from a few micrometres to a few nanometers; we'll concentrate on devices rather than fundamental physical effects, which come in a wide range.Micro-optics are optical systems with a size ranging from a few micrometres to a millimetre. Small lenses or arrays of lenses, as well as optical fibres with a microscale core diameter, fall under this category. Integrated optics requires such small optical components. Traditional angle measurement tools such as Micro Optic Theodolites are used in geodesic survey and engineering measurement. Geodesic survey is one of the applications for this tool. Engineers use it to make measurements. In construction, this tool is used for all regular surveying.
Track 17 : Quantum Photonics
Quantum photonics is the science of creating, controlling, and detecting light in regimes where individual quanta of the light field may be coherently controlled (photons). The EPR paradox and Bell test experiments, for example, have used quantum photonics to investigate quantum phenomena. Quantum photonics is also predicted to play a crucial role in the development of future technologies including quantum computing, quantum key distribution, and quantum metrology. Photonic integrated circuits are used in integrated quantum photonics to control photonic quantum states for applications in quantum technology. Integrated quantum photonics offers a possible method for scaling up and miniaturising optical quantum circuits. Quantum technology, such as quantum computing, quantum communication, quantum simulation, quantum walking, and quantum metrology, is a prominent application of integrated quantum photonics.Integrated quantum photonics is the application of photonic integrated circuit technology to quantum photonics, and it is regarded as a crucial step in the development of practical quantum technology. Compared to bulk optics, photonic chips have the following advantages:
- Miniaturization - Smaller system sizes result in significant reductions in size, weight, and power consumption.
- Stability - Waveguides and components manufactured using modern lithographic processes are phase stable (coherent) and do not require optical alignment.
- Experiment size - A device of a few square centimetres can accommodate a large number of optical components.
- Manufacturability - Devices may be mass produced with minimal cost increase.
Laser, Optics and Photonics Technology is one of the growing fields and scope of Optics and Laser Technology involves in several areas such as development in optoelectronic devices & photonics, Optical instruments & components. It has many Medical applications mainly in the field of Ophthalmology, Radiology, Dentistry, and Dermatology and it also have many Industrial applications. The industrial applications are Laser cutting, Laser welding, Laser scribing etc. This is not only used in medical field but also used in communication, Military operation. At present the Laser Technology market is around $7 billion and it is expected to grow up to $17.06 billion by the year 2020. According to the new market research report on the "Laser Technology Market by Application , Vertical & Geography - Global Forecast to 2022", this market is expected to be valued at USD 15.38 Billion by 2022, at a CAGR of 5.2% between 2017 and 2022. The major factors driving the growth of the laser technology market include increasing demand from the healthcare sector and shift towards production of Nano and micro devices, and enhanced performance over the traditional material processing techniques.
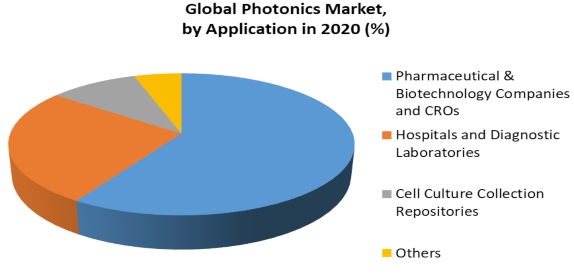
The global adaptive optics market is expected to reach USD 7,666.4 Million by 2020, at a CAGR of 99.4% between 2015 and 2020. The military & defense sector was the largest contributor to the overall adaptive optics market, accounting for a share of 56.1% in 2014. The biomedical sector accounted for a share of 21.7% of the market in 2014. The Americas accounted for the largest share of 44.0% of the Adaptive optics market in 2014; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 94.0% between 2015 and 2020. The Global Photonics Market was valued at USD 589.82 billion in 2020, and it is expected to reach USD 1019.77 billion by 2026, registering a CAGR of approximately 7.14% during the period of 2021-2026. The COVID-19 outbreak has affected many industries. Due to the nationwide lockdown globally, many photonic devices manufacturing companies face supply chain interruption and manufacturing inefficiency. However, the COVID-19 outbreak has expanded the scope of photonic devices in the healthcare industry.
According to the new market research report “Silicon Photonics Market by Component (Optical Waveguides, Optical Modulators, Photo Detectors, WDM, Lasers), Product (Transceivers, Active Optical Cables, Multiplexers, and Attenuators), Application, and Geography - Global Forecast to 2022”, this market is expected to be worth USD 1,078.9 Million by 2022, at a CAGR of 22.1% between 2016 and 2022. The major driver for the growth of the silicon photonics market is the increasing use in data communication applications. The silicon photonics market in APAC is expected to grow at the highest CAGR between 2016 and 2022.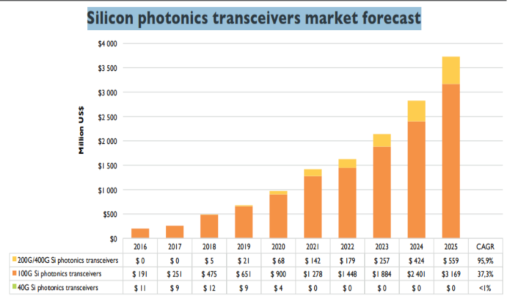
Benefits of Participation for Speaker
- Worldwide appreciation of the profile of Researchers.
- Obtain credits for professional growth.
- Explore the latest of cutting edge analysis.
- Make long-term bonds at social and networking activities.
- An ability to advertise one page in the distribution of abstract books and flyers that ultimately gets 1 million views and adds great value to your research profile.
- Learn a transition beyond your area of interest to learn more about new subjects and studies away from your core subject of Laser Optics.
- We have distinctive networking, learning and enjoyable integration into a single package.
Benefits of Participation for Delegate
- Professional Development-Improve understanding and knowledge.
- Your participation will help us with a new methodology and ideology that can be used to broaden the outcomes of businesses or industries.
- Opportunities for Laser Optics Summit researchers and experts in the same field to meet and exchange new ideas.
Benefit of Participation for Sponsor
- Exposure to the international environment would increase the possibility of new companies.
- Opportunity to demonstrate your company's latest technologies, new products, or service your business to a wide range of international participants.
- Increase business by our participants through lead generation.
- It takes a lot of time, effort and drive to create a successful company, so it's always nice to have a network of colleagues and associates to draw energy from individuals who share a common drive and objective.
- Benchmarking main organization plans and moving it forward.
- Get feedback from trustworthy people at our webinar to your company questions and challenges.
- On our banner, website and other proceedings, branding and marketing content, the advertising logo of your company.
Benefit of Association for Collaborators
- Nobody has this massive visitors to Laser Optics in the world, this is the best forum to highlight society.
- Creating long-lasting peer relationships.
- In our banner, website and other proceedings, branding and marketing material, promotional content and your Organization logo will increase your number of subscribers/members by 40%.
- The exposure of our event to your Company listing in the Global Business forum will have a great effect on your association.
- Your representatives can network to update their knowledge and understanding of your organisation and services with key delegates.
- Laser Optics advertising materials such as posters, brochures, pamphlets, services that will be circulated to hospitals, universities, society and researchers will be integrated with information.
Conference Highlights
- Laser System
- Optics and Lasers in Medicine
- Optoelectronics
- Optical Communications and Networking
- Advancements in Photonics
- Nano Photonics and Bio Photonics
- Quantum Science and Technology
- Technologies in Lasers, Optics and Photonics
- Applications and Trends in Optics and Photonics
- Fiber Laser Technology
- Optical physics
- Optical Fiber
- Surface Enchanced Spectroscopy
- Bio and Medical Optics
- Optical Engineering
- Nano and Micro Optics
- Quantum Photonics
- Laser Applications in Polymers
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 24-25, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



















